LeetCode: Graphs II 01 BFS
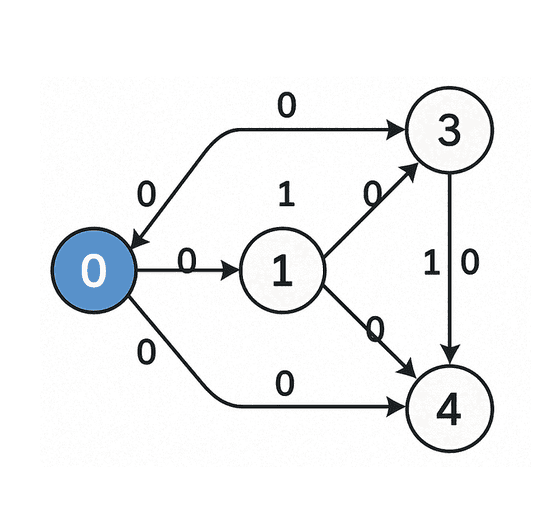
Zero One BFS Algorithm Intro
Intro
01 BFS is an efficient shortest path algorithm for graphs where edge weights are only 0 or 1
Special case of BFS/Dijkstras
Instead of using a standard priority queue, it uses a deque to achieve O(V + E) time
Efficiently computes shortest distances from a single source in such graphs
Graph Requirements
- Weighted graph with edge weights only 0 or 1 only
- Directed or Undirected
- Represented Using:
- Adjacency List
Output
Shortest distance from the source node to all other nodes Optionally, the path itself
Video Animation
written: https://codeforces.com/blog/entry/22276
Pseudo Code
from collections import deque
def zero_one_bfs(graph, source):
n = len(graph)
dist = [float('inf')] * n
dist[source] = 0
dq = deque()
dq.append(source)
while dq:
node = dq.popleft()
for neighbor, weight in graph[node]:
if dist[node] + weight < dist[neighbor]:
dist[neighbor] = dist[node] + weight
if weight == 0:
dq.appendleft(neighbor) # 0-weight edges prioritized
else:
dq.append(neighbor) # 1-weight edges go to back
return distTime Complexity
Each vertex is processed at most once Each edge is considered at most once
Must faster than Dijkstras for this specific case O(E + V) instead of O(E log V)
Space Complexity
Distance Array: O(V) Deque: O(V) in worst case
IRL Use Case
-
Special Graphs Slide (0 cost) vs Step (1 cost)
-
Network Propagation With Free/Paid Edges 0 for instance transfer, 1 for delayed transfer
2290. Minimum Obstacle Removal to Reach Corner ::1:: - Hard
Topics: Array, Breadth First Search, Graph Theory, Heap (Priority Queue), Matrix, Shortest Path
Intro
You are given a 0-indexed 2D integer array grid of size m x n. Each cell has one of two values: 0 represents an empty cell, 1 represents an obstacle that may be removed. You can move up, down, left, or right from and to an empty cell. Return the minimum number of obstacles to remove so you can move from the upper left corner (0, 0) to the lower right corner (m - 1, n - 1).
| Example Input | Output |
|---|---|
| grid = [[0,1,1],[1,1,0],[1,1,0]] | 2 |
| grid = [[0,1,0,0,0],[0,1,0,1,0],[0,0,0,1,0]] | 0 |
Constraints:
m == grid.length
n == grid[i].length
1 ≤ m, n ≤ 10^5
2 ≤ m*n ≤ 10^5
grid[i][j] is either 0 or 1
grid[0][0] == grid[m-1][n-1] == 0
Abstraction
Given a graph full of empty cell or obstacles, determine the minimum number of obstacles to remove to move from top left to bottom right
Space & Time Complexity
| Solution | Time Complexity | Space Complexity | Time Remark | Space Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bug | Error |
|---|---|
Brute Force:
| Aspect | Time Complexity | Space Complexity | Time Remarks | Space Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Find the Bug:
Solution 1: [01 BFS] 01 BFS Approach - Advanced Graphs/Advanced Graphs
def minimumObstacles(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
# Grid dimensions
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
# Directions: up, down, left, right
directions = [(1,0), (-1,0), (0,1), (0,-1)]
# distance matrix: min obstacles removed to reach each cell
dist = [[float('inf')] * n for _ in range(m)]
dist[0][0] = grid[0][0] # starting cost (remove if starting on 1)
# deque for 0-1 BFS
dq = deque()
dq.append((0,0))
while dq:
r, c = dq.popleft()
# Explore neighbors
for dr, dc in directions:
nr, nc = r + dr, c + dc
# Valid boundaries
if 0 <= nr < m and 0 <= nc < n:
# New distance = current + cost to enter neighbor
new_dist = dist[r][c] + grid[nr][nc]
# Relaxation
if new_dist < dist[nr][nc]:
dist[nr][nc] = new_dist
# 0-cost move → appendleft
if grid[nr][nc] == 0:
dq.appendleft((nr, nc))
# 1-cost move → append to back
else:
dq.append((nr, nc))
# Result: min obstacles to remove to reach bottom-right
return dist[m-1][n-1]1368. Minimum Cost to Make at Least One Valid Path in a Grid ::1:: - Hard
Topics: Array, Breadth First Search, Graph Theory, Heap (Priority Queue), Matrix, Shortest Path
Intro
Given an m x n grid. Each cell of the grid has a sign pointing to the next cell you should visit if you are currently in this cell. The sign of grid[i][j] can be: 1 which means go to the cell to the right. (i.e go from grid[i][j] to grid[i][j + 1]) 2 which means go to the cell to the left. (i.e go from grid[i][j] to grid[i][j - 1]) 3 which means go to the lower cell. (i.e go from grid[i][j] to grid[i + 1][j]) 4 which means go to the upper cell. (i.e go from grid[i][j] to grid[i - 1][j]) Notice that there could be some signs on the cells of the grid that point outside the grid. You will initially start at the upper left cell (0, 0). A valid path in the grid is a path that starts from the upper left cell (0, 0) and ends at the bottom-right cell (m - 1, n - 1) following the signs on the grid. The valid path does not have to be the shortest. You can modify the sign on a cell with cost = 1. You can modify the sign on a cell one time only. Return the minimum cost to make the grid have at least one valid path.
| Example Input | Output |
|---|---|
| grid = [[1,1,1,1],[2,2,2,2],[1,1,1,1],[2,2,2,2]] | 3 |
| grid = [[1,1,3],[3,2,2],[1,1,4]] | 0 |
| grid = [[1,2],[4,3]] | 1 |
Constraints:
m == grid.length
n == grid[i].length
1 ≤ m, n ≤ 100
1 ≤ grid[i][j] ≤ 4
Abstraction
What the heck!
Space & Time Complexity
| Solution | Time Complexity | Space Complexity | Time Remark | Space Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bug | Error |
|---|---|
Brute Force:
| Aspect | Time Complexity | Space Complexity | Time Remarks | Space Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Find the Bug:
Solution 1: [01 BFS] 01 BFS Approach - Advanced Graphs/Advanced Graphs
def minCost(self, grid):
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
# directions: right, left, down, up
dirs = [(0,1), (0,-1), (1,0), (-1,0)]
# visited[i][j] = minimum cost to reach (i,j)
visited = [[float('inf')] * n for _ in range(m)]
visited[0][0] = 0
dq = deque()
dq.append((0,0,0)) # i, j, cost
while dq:
i, j, cost = dq.popleft()
for d, (dx, dy) in enumerate(dirs, start=1):
ni, nj = i + dx, j + dy
if 0 <= ni < m and 0 <= nj < n:
# If we follow the arrow, cost = 0; otherwise cost = 1
new_cost = cost if d == grid[i][j] else cost + 1
if new_cost < visited[ni][nj]:
visited[ni][nj] = new_cost
if d == grid[i][j]:
dq.appendleft((ni, nj, new_cost)) # 0-cost → front
else:
dq.append((ni, nj, new_cost)) # 1-cost → back
return visited[m-1][n-1]